Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
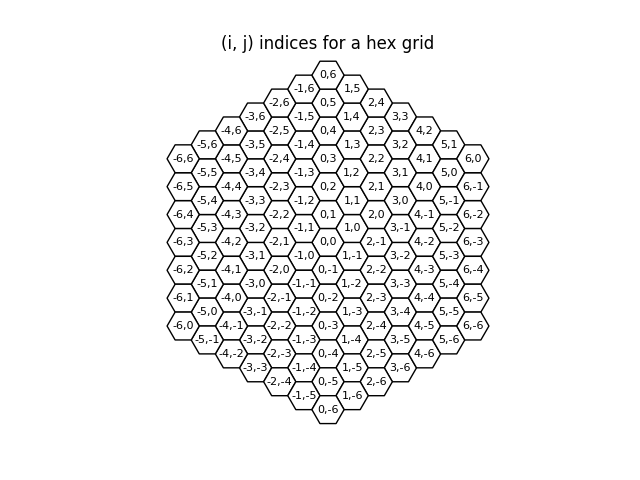
Make a hex grid.
This uses a grid factory method to build an infinite 2-D grid of hexagons with pitch equal to 1.0 cm.
Learn more about grids.
import math
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import PatchCollection
from armi import configure
from armi.reactor import grids
configure(permissive=True)
hexes = grids.HexGrid.fromPitch(1.0)
polys = []
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
ax.set_axis_off()
for hex_i in hexes.generateSortedHexLocationList(127):
x, y, z = hex_i.getGlobalCoordinates()
ax.text(x, y, f"{hex_i.i},{hex_i.j}", ha="center", va="center", fontsize=8)
polys.append(mpatches.RegularPolygon((x, y), numVertices=6, radius=1 / math.sqrt(3), orientation=math.pi / 2))
patches = PatchCollection(polys, fc="white", ec="k")
ax.add_collection(patches)
# create a bounding box around patches with a small margin (2%)
bbox = patches.get_datalim(ax.transData)
bbox = bbox.expanded(1.02, 1.02)
ax.set_xlim(bbox.xmin, bbox.xmax)
ax.set_ylim(bbox.ymin, bbox.ymax)
ax.set_title("(i, j) indices for a hex grid")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.133 seconds)